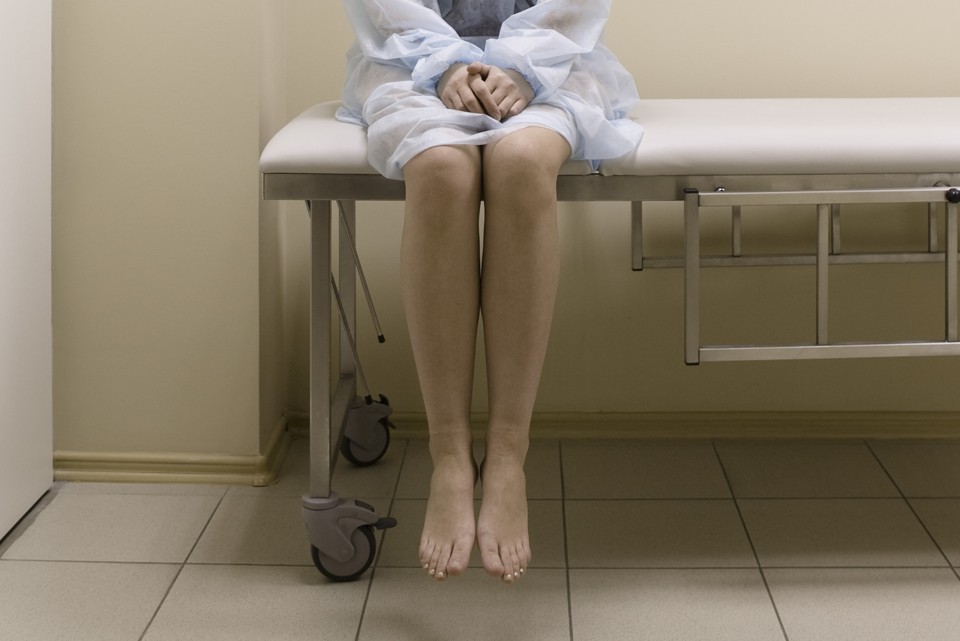
Early on a Wednesday morning, I heard an anguished cry—then silence.
I rushed into the bedroom and watched my wife, Rachel, stumble from the bathroom, doubled over, hugging herself in pain.
“Something’s wrong,” she gasped.
This scared me. Rachel’s not the type to sound the alarm over every pinch or twinge. She cut her finger badly once, when we lived in Iowa City, and joked all the way to Mercy Hospital as the rag wrapped around the wound reddened with her blood. Once, hobbled by a training injury in the days before a marathon, she limped across the finish line anyway.
So when I saw Rachel collapse on our bed, her hands grasping and ungrasping like an infant’s, I called the ambulance. I gave the dispatcher our address, then helped my wife to the bathroom to vomit.
I don’t know how long it took for the ambulance to reach us that Wednesday morning. Pain and panic have a way of distorting time, ballooning it, then compressing it again. But when we heard the sirens wailing somewhere far away, my whole body flooded with relief.
“Eleven,” Rachel croaked.
As we loaded into the ambulance, here’s what we didn’t know: Rachel had an ovarian cyst, a fairly common thing. But it had grown, undetected, until it was so large that it finally weighed her ovary down, twisting the fallopian tube like you’d wring out a sponge. This is called ovarian torsion, and it creates the kind of organ-failure pain few people experience and live to tell about.
“Ovarian torsion represents a true surgical emergency,” says an article in the medical journal Case Reports in Emergency Medicine. “High clinical suspicion is important. … Ramifications include ovarian loss, intra-abdominal infection, sepsis, and even death.” The best chance of salvaging a torsed ovary is surgery within eight hours of when the pain starts.
* * *
There is nothing like witnessing a loved one in deadly agony. Your muscles swell with the blood they need to fight or run. I felt like I could bend iron, tear nylon, through the 10-minute ambulance ride and as we entered the windowless basement hallways of the hospital.
And there we stopped. The intake line was long—a row of cots stretched down the darkened hall. Someone wheeled a gurney out for Rachel. Shaking, she got herself between the sheets, lay down, and officially became a patient.
Emergency-room patients are supposed to be immediately assessed and treated according to the urgency of their condition. Most hospitals use the Emergency Severity Index, a five-level system that categorizes patients on a scale from “resuscitate” (treat immediately) to “non-urgent” (treat within two to 24 hours).
“She’ll have to wait her turn,” she said. Other nurses’ reactions ranged from dismissive to condescending. “You’re just feeling a little pain, honey,” one of them told Rachel, all but patting her head.
We didn’t know her ovary was dying, calling out in the starkest language the body has. I saw only the way Rachel’s whole face twisted with the pain.
Soon, I started to realize—in a kind of panic—that there was no system of triage in effect. The other patients in the line slept peacefully, or stared up at the ceiling, bored, or chatted with their loved ones. It seemed that arrival order, not symptom severity, would determine when we’d be seen.
As we neared the ward’s open door, a nurse came to take Rachel’s blood pressure. By then, Rachel was writhing so uncontrollably that the nurse couldn’t get her reading.
She sighed and put down her squeezebox.
“You’ll have to sit still, or we’ll just have to start over,” she said.
Finally, we pulled her bed inside. They strapped a plastic bracelet, like half a handcuff, around Rachel’s wrist.
* * *
From an early age we’re taught to observe basic social codes: Be polite. Ask nicely.Wait your turn. But during an emergency, established codes evaporate—this is why ambulances can run red lights and drive on the wrong side of the road. I found myself pleading, uselessly, for that kind of special treatment. I kept having the strange impulse to take out my phone and call 911, as if that might transport us back to an urgent, responsive world where emergencies exist.
By 10 a.m., Rachel’s cot had moved into the “red zone” of the E.R., a square room with maybe 30 beds pushed up against three walls. She hardly noticed when the attending physician came and visited her bed; I almost missed him, too. He never touched her body. He asked a few quick questions, and then left. His visit was so brief it didn’t register that he was the person overseeing Rachel’s care.
Around 10:45, someone came with an inverted vial and began to strap a tourniquet around Rachel’s trembling arm. We didn’t know it, but the doctor had prescribed the standard pain-management treatment for patients with kidney stones: hydromorphone for the pain, followed by a CT scan.
The pain medicine started seeping in. Rachel fell into a kind of shadow consciousness, awake but silent, her mouth frozen in an awful, anguished scowl. But for the first time that morning, she rested.
She was talking about Rachel.
“That to me felt like this deeply personal and deeply upsetting embodiment of what was at stake,” she said. “Not just on the side of the medical establishment—where female pain might be perceived as constructed or exaggerated—but on the side of the woman herself: My friend has been reckoning in a sustained way about her own fears about coming across as melodramatic.”
“Female pain might be perceived as constructed or exaggerated”: We saw this from the moment we entered the hospital, as the staff downplayed Rachel’s pain, even plain ignored it. In her essay, Jamison refers back to “The Girl Who Cried Pain,” a study identifying ways gender bias tends to play out in clinical pain management. Women are “more likely to be treated less aggressively in their initial encounters with the health-care system until they ‘prove that they are as sick as male patients,’” the study concludes—a phenomenon referred to in the medical community as “Yentl Syndrome.”
I felt certain of this: The diagnosis of kidney stones—repeated by the nurses and confirmed by the attending physician’s prescribed course of treatment—was a denial of the specifically female nature of Rachel’s pain. A more careful examiner would have seen the need for gynecological evaluation; later, doctors told us that Rachel’s swollen ovary was likely palpable through the surface of her skin. But this particular ER, like many in the United States, had no attending OB-GYN. And every nurse’s shrug seemed to say, “Women cry—what can you do?”
Nationwide, men wait an average of 49 minutes before receiving an analgesic for acute abdominal pain. Women wait an average of 65 minutes for the same thing. Rachel waited somewhere between 90 minutes and two hours.
“My friend has been reckoning in a sustained way about her own fears about coming across as melodramatic.” Rachel does struggle with this, even now. How long is it appropriate to continue to process a traumatic event through language, through repeated retellings? Friends have heard the story, and still she finds herself searching for language to tell it again, again, as if the experience is a vast terrain that can never be fully circumscribed by words. Still, in the throes of debilitating pain, she tried to bite her lip, wait her turn, be good for the doctors.
Eventually, the doctor—the man who’d come to Rachel’s bedside briefly, and just once—packed his briefcase and left. He’d been around the ER all day, mostly staring into a computer. We only found out later he’d been the one with the power to rescue or forget us.
When a younger woman came on duty to take his place, I flagged her down. I told her we were waiting on the results of a CT scan, and I hassled her until she agreed to see if the results had come in.
When she pulled up Rachel’s file, her eyes widened.
“What is this mess?” she said. Her pupils flicked as she scanned the page, the screen reflected in her eyes.
“Oh my god,” she murmured, as though I wasn’t standing there to hear. “He never did an exam.”
The male doctor had prescribed the standard treatment for kidney stones—Dilauded for the pain, a CT scan to confirm the presence of the stones. In all the hours Rachel spent under his care, he’d never checked back after his initial visit. He was that sure. As far as he was concerned, his job was done.
“She has a large mass in her abdomen,” the female doctor said. “We don’t know what it is.”
That’s when we lost it. Not just because our minds filled then with words liketumor and cancer and malignant. Not just because Rachel had gone half crazy with the waiting and the pain. It was because we’d asked to wait our turn all through the day—longer than a standard office shift—only to find out we’d been an emergency all along.
Suddenly, the world responded with the urgency we wanted. I helped a nurse push Rachel’s cot down a long hallway, and I ran beside her in a mad dash to make the ultrasound lab before it closed. It seemed impossible, but we were told that if we didn’t catch the tech before he left, Rachel’s care would have to be delayed until morning.
“Whatever happens,” Rachel told me while the tech prepared the machine, “don’t let me stay here through the night. I won’t make it. I don’t care what they tell you—I know I won’t.”
Soon, the tech was peering inside Rachel through a gray screen. I couldn’t see what he saw, so I watched his face. His features rearranged into a disbelieving grimace.
By then, Rachel and I were grasping at straws. We thought: cancer. We thought: hysterectomy. Lying there in the dim light, Rachel almost seemed relieved.
After the ultrasound, we led the gurney—slowly, this time—down the long hall to the ER, which by then was completely crammed with beds. Trying to find a spot for Rachel’s cot was like navigating rush-hour traffic.
Then came more bad news. At 8 p.m., they had to clear the floor for rounds. Anyone who was not a nurse, or lying in a bed, had to leave the premises until visiting hours began again at 9.
When they let me back in an hour later, I found Rachel alone in a side room of the ER. So much had happened. Another doctor had told her the mass was her ovary, she said. She had something called ovarian torsion—the fallopian-tube twists, cutting off blood. There was no saving it. They’d have to take it out.
Rachel seemed confident and ready.
“He’s a good doctor,” she said. “He couldn’t believe that they left me here all day. He knows how much it hurts.”
When I met the surgery team, I saw Rachel was right. Talking with them, the words we’d used all day—excruciating, emergency, eleven—registered with real and urgent meaning. They wanted to help.
By 10:30, everything was ready. Rachel and I said goodbye outside the surgery room, 14 and a half hours from when her pain had started.
* * *
Rachel’s physical scars are healing, and she can go on the long runs she loves, but she’s still grappling with the psychic toll—what she calls “the trauma of not being seen.” She has nightmares, some nights. I wake her up when her limbs start twitching.
Sometimes we inspect the scars on her body together, looking at the way the pink, raised skin starts blending into ordinary flesh. Maybe one day, they’ll become invisible. Maybe they never will.




